Electric vehicles do seem to be quite intriguing and considering the advantages they bring to the table if some alien race visited us, it would be puzzled to learn that we’re still reticent to fully committing to it. However, we’re humans and we have our own whims to keep us back from doing the right thing.
Range anxiety is the big no-no to be followed by such issues like the lack of excitement, vibrations and a feel of torque building up under our right foot. On the same list we could include charging too. Apart from the fact that it takes too long on some cars, it also demands you leaving your car attached to a power cable for a reasonable amount of time.
Yeah, it’s not a pretty sight and a lot of people have a problem with leaving their car and cable out in the open like that. The solution? Wireless charging, of course.
You’ve heard about it for quite some time and it has been in use, especially in the smartphone industry. Now manufacturers are looking into it to make their cars easier to recharge.
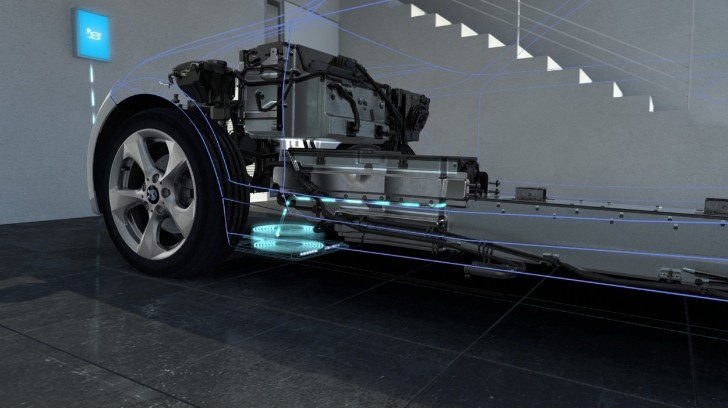
BMW showed us their take on the matter at the 2015 Consumer Electronics Show. Their system is comprised of a primary and a secondary coil that work together.
The primary coil is fitted in a base pad underneath the vehicle while the secondary coil is integrated in the underside of the i8 for example. When the car is in place, right above the base pad, the charging process begins.
In the future, the charge rate is expected to go higher, up to 7 kW for cars with larger batteries, such as the i3, for example. If you’re worried about the electromagnetic field around the car you should know that its strength is well below the existing regulatory limits.
The system also has plenty of protection features on, to make sure no accidents can happen. In case there’s water or snow on the coil, it won’t work and the same applies in case the two coils aren’t perfectly aligned or if an object lies between them.
Yeah, it’s not a pretty sight and a lot of people have a problem with leaving their car and cable out in the open like that. The solution? Wireless charging, of course.
You’ve heard about it for quite some time and it has been in use, especially in the smartphone industry. Now manufacturers are looking into it to make their cars easier to recharge.
BMW showed us their take on the matter at the 2015 Consumer Electronics Show. Their system is comprised of a primary and a secondary coil that work together.
The primary coil is fitted in a base pad underneath the vehicle while the secondary coil is integrated in the underside of the i8 for example. When the car is in place, right above the base pad, the charging process begins.
How does it work?
An alternating magnetic field is generated which transmits electricity between the coils. The electricity is transmitted without cables or contacts across a gap of a couple of inches, at a charge rate of 3.3 kW. The high-voltage battery of the BMW i8 can be fully recharged in less than two hours using this system – which is approximately the same amount of time required with a wired connection.In the future, the charge rate is expected to go higher, up to 7 kW for cars with larger batteries, such as the i3, for example. If you’re worried about the electromagnetic field around the car you should know that its strength is well below the existing regulatory limits.
The system also has plenty of protection features on, to make sure no accidents can happen. In case there’s water or snow on the coil, it won’t work and the same applies in case the two coils aren’t perfectly aligned or if an object lies between them.